Advanced Java, J2EE : Day 3
Spring
Lightweight framework for building Enterprise Application, build on Concept of DI [Inversion of Control]
SOLID Responsibility
→ S → Single Responsibilty
→ O → Open Close Principle [Closed for change, Open for extension]
→ L → Liskov Substitution Principle
→ I → Interface Segregation
→ D → Dependency Injection
Why Spring
Dependency Management
Spring is not the only one which provides DI. Engine also do that but only limited services and not user defined services
AOP : Aspect oriented programming
Cross cutting concern leading to code tangling(Business Logic → Aspect Code→ BL→AC) and code scattering. Aspect(Transaction, Security, Logging)
EAI : Enterprise Application Integration
Loosely Coupled and easy to test
Main Concepts of Spring
Dependency Injection
It is a process whereby objects define their dependencies (that is, the other objects they work with) only through constructor arguments, arguments to a factory method, or properties that are set on the object instance after it is constructed or returned from a factory method. The container then injects those dependencies when it creates the bean. This process is fundamentally the inverse (hence the name, Inversion of Control) of the bean itself controlling the instantiation or location of its dependencies by using direct construction of classes or a mechanism such as the Service Locator pattern.
The org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container. BeanFactory and ApplicationContext provides configuration mechanism
BeanFactory interface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object. ApplicationContext is a sub-interface of BeanFactory(Application-layer specific contexts such as the WebApplicationContext for use in web applications, Event publication, Message resource handling, Easier integration with Spring’s AOP features)
Beans
Any object managed managed by Spring Container. It is Object that is instantiated, assembled, and managed by a Spring IoC container
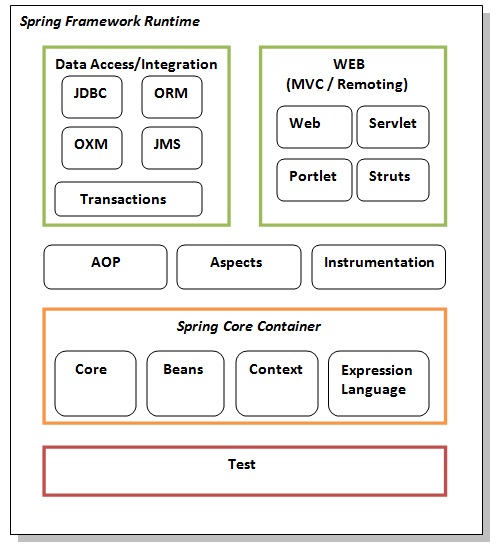
The Spring framework comprises of many modules such as core, beans, context, expression language, AOP, Aspects, Instrumentation, JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS, Transaction, Web, Servlet, Struts etc. These modules are grouped into Test, Core Container, AOP, Aspects, Instrumentation, Data Access / Integration, Web
Beans, and the dependencies among them, are reflected in the configuration metadata.
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext or FileSystemXmlApplicationContext for XML or Annotation Based(Spring 2.5), Java Based(Spring 3.0)
XML-based configuration metadata configures these beans as <bean/> elements inside a top-level <beans/> element. Java configuration typically uses @Bean-annotated methods within a @Configuration class.

Instantiating a Container
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
Using the Container
ApplicationContext lets you read bean definitions and access them
// create and configure beans
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
// retrieve configured instance
PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class);
// use configured instance
List<String> userList = service.getUsernameList();
Type of DI
-
Constructor-based Dependency Injection
public class SimpleMovieLister { // the SimpleMovieLister has a dependency on a MovieFinder private final MovieFinder movieFinder; // a constructor so that the Spring container can inject a MovieFinder public SimpleMovieLister(MovieFinder movieFinder) { this.movieFinder = movieFinder; } // business logic that actually uses the injected MovieFinder is omitted... } -
Setter-based Dependency Injection
public class SimpleMovieLister { // the SimpleMovieLister has a dependency on the MovieFinder private MovieFinder movieFinder; // a setter method so that the Spring container can inject a MovieFinder public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) { this.movieFinder = movieFinder; } // business logic that actually uses the injected MovieFinder is omitted... }
A lazy-initialized bean tells the IoC container to create a bean instance when it is first requested, rather than at startup.
lazy-init="true"
Autowiring
Spring container can autowire relationships between collaborating beans
Scope
Spring supports 6 beans. singleton, prototype, request, session, application, websocket
Different Stereotypes
→@Component is a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component. @Repository, @Service, and @Controller are specializations of @Component
→ @Service
→ @Controller in
→ @Repository annotation is a marker for any class that fulfills the role or stereotype of a repository (also known as Data Access Object or DAO)
→ @RestController annotation from Spring MVC is composed of @Controller and @ResponseBody.
Repository
The @Repository annotation is a marker for any class that fulfills the role or stereotype of a repository (also known as Data Access Object or DAO).
EL: It is an extension to the EL defined in JSP. It provides support to setting and getting property values, method invocation, accessing collections and indexers, named variables, logical and arithmetic operators, retrieval of objects by name etc.
Metadata using xml
setter injection and constructor injection
<bean id="studentbean" class="com.javatpoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Ashish Jha"></property>
</bean>
The instrumentation module provides support to class instrumentation and classloader implementations.
Metadata using Annotation
Part of Java Source Code, no need to toggle between XML and Java
Javac knows annotation, XML needs SAX or DOM parser
IOC Container
responsible to instantiate, configure and assemble the objects. There are two types of IoC containers
- BeanFactory
- ApplicationContext
Spring Container creates object using following annotations. Scope or liftime could be session, request or singleton. By default it is singelton
@Component : generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component.
@Repository : use sql-error-codes.xml to throw meaningful error code with messaged, annotates classes at the persistence layer, which will act as a database repository.
@Service: annotates classes at the service layer.
@Controller : class level annotation which tells the Spring Framework that this class serves as a controller in Spring MVC:
@RestController
@Configuration : Contain bean definition methods annotated with @Bean:
CGLib → JavaAssist → Byte Buddy : Changes Byte Cide
Autowiring feature of spring framework enables you to inject the object dependency implicitly. It internally uses setter or constructor injection.
@RequestMapping.
Simply put, the annotation is used to map web requests to Spring Controller methods.
ORM : Object Relational Mapping
ORM → Once Mapping is done, DDL and DML can be performed
ORM Framework : Hibernate, TopLink, Kodo, EclipseLink, openJPA, JDO
JPA ==> Java Persistence API ==> Specification for ORM
ORM provides a layer over JDBC
JPA is interface(Specification) over ORM.
ORM creates persistence context(Entities are managed)
DataSource → pool of database connections
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
cpds.setDriverClass( "org.postgresql.Driver" ); //loads the jdbc driver
cpds.setJdbcUrl( "jdbc:postgresql://localhost/testdb" ); cpds.setUser("swaldman");
cpds.setPassword("test-password");
// the settings below are optional
//c3p0 can work with defaults cpds.setMinPoolSize(5);
cpds.setAcquireIncrement(5);
cpds.setMaxPoolSize(20);
props.setProperty("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect");
em.save(p); // generate INSERT statement
em.createQuery("from Product"); // generate SELECT
To generate SQL for MySQL8
props.setProperty("hibnernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "update");
HBM ==> Hibernate Mapping
DDL ==> Data Definition Language [ CREATE, DROP, ALTER]
Transaction Management
Transaction management can be programatic or declarative.
Declarative Transaction == > @EnableTransactionManagement
// JDBC
public void transferFunds(Account fromAcc, Account toAcc, double amt) {
Connection con = ...
try{
con.setAutoCommit(false);
PS1 ==> to update "fromACC"
PS2 ==> to update "toACC"
PS3 ==> "insert into bank_tansaction table"
con.commit();
} catch(SQLException ex) { con.rollback(); } }
// Hibernate
public void transferFunds(Account fromAcc, Account toAcc, double amt) {
Session ses = SessionFactory.getSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try{
tx = ses.beginTransaction();
PS1 ==> to update "fromACC"
PS2 ==> to update "toACC"
PS3 ==> "insert into bank_tansaction table"
tx.commit();
} catch(SQLException ex) { tx.rollback(); }
@Transactional
public void transferFunds(Account fromAcc, Account toAcc, double amt) { actual CRUD without tx code }
within the method if no exception occurs ==> commit happens if exception occurs ==> Rollback
@Transactional(rollBackFor=InsufficientBalanceException.class, noRollBackFor=ArrayIndexOutOfBounds.Exception)
JPQL : Java persistence Query Language
em.remove(p); // delete SQL
em.merge(p); // update SQL
@Controller
public class ProductController {
@Autowired OrderService orderService;
@RequestMapping("getProducts.do")
ModelAndView method1() {
interact with service ==> DAO ==> DB
}
@RequestMapping("addProduct.do")
ModelAndView method2() {
}
MVC → DispatcherServlet, @controller ModelAndView